|
 Instruction > Instructional Design > LMS - LCMS Instruction > Instructional Design > LMS - LCMS
Instructional Design
"A good educational system should...provide all who want to learn with access to available resources at any time in their lives; empower all who want to share what they know to find those who want to learn it from them...."
Ivan Illich (1971)
|
Virtual Learning Environments: online software
There are at least four layers of learner interaction and experience in a Virtual Learning Environment: Portal, LMS, Course and Lesson delivery. Click on the graphic to see a larger version of the illustration.

|
Virtual Learning Environments
|
| 1. Portal Site |
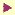 Learning Community Support Learning Community Support
 Announcments, News, Calendar Announcments, News, Calendar
 Web services & applications Web services & applications |
2. Learning Management
System (LMS) |
 Personalized Student Portal (individual student plan, Personalized Student Portal (individual student plan,
records, progress reports, personal links to courses)
 Navigate to program resources & course catalogue Navigate to program resources & course catalogue
 Enrollment in courses Enrollment in courses |
| 3. Course Web Pages |
 Instructor posting of course syllabus, plan, assignments, Instructor posting of course syllabus, plan, assignments,
calendar, lesson & activity pages,
 Links to tutorials, virtual classroom sessions, discussion Links to tutorials, virtual classroom sessions, discussion
forum, tests, and collaboration
|
4. Lesson Instructional
Delivery |
 Virtual Classroom sessions Virtual Classroom sessions
 Discussion Forum Discussion Forum
 Self-paced Tutorials Self-paced Tutorials
 Tests, Quizzes, Surveys Tests, Quizzes, Surveys
 Social Networking & Collaboration Social Networking & Collaboration
 Lesson specific instructional media Lesson specific instructional media
(static, interactive, rich media, & social) |
Learning Management System (LMS)
Learning Management Systems (LMS) provide an infrastructure platform through which learning content is delivered and managed. It provides a combination of software tools that perform a viarety of functions related to online and offline training administration and performance managment.
Typically, an LMS is an internet-based software that
- Deploys
- Manages
- Tracks
- Reports on
the interaction between the learner and the content, and the learner and the instructor.
Learner and content interaction, includes:
- Student registration in program
- Enrollment in specific courses and special activities
- Entry and re-entry into online learning space: WBT, virtual classroom, learning labs, etc.
- Tracking participation & progress
- Recording scores: quiz, test, final evaluation
- Documenting status, completion & certification
Learner and instructor interaction, includes:
- Publishing and receiving communication --
- email
- instant messaging
- threaded discussion
- chat
- personal mentoring through online learning space: virtual classroom, learning labs, etc.
- Posting
- announcements
- course descriptions & syllabus
- course requirements & pre-requisites
- assignments & activity schedule
- Eliciting feedback from students and faculty
Learning Management Systems (LMS) perform student registration, course enrollment, course presentation, student bookmarking, track learner progress, record test scores, and indicate course completions, and finally allow instructor trainers to assess the performance of their students.
Here is an illustration of an LMS system diagram that uses the SCORM protocol developed by ADL to deliver SCOs (Shareable Content Objects). See the discussion on Learning Objects for an explaination of SCORM.

Some of the current LMS products and vendors in 2007 include:
Learning Content Management System (LCMS) 
A Learning Content Management System (LCMS) is a multi-user environment where learning developers may create, store, reuse, manage, and deliver digital learning content from a central object repository.
LCMS products allow users, such as administrators, authors, instructors and subject matter experts, to create new instructional content, or to upload existing 3rd party instructional content. The LCMS manages the organization of content — curriculum, courses, modules, learning objects, and units of digital learning content/assets
Digital assets includes products such as MS Word & text documents, PowerPoint slides, Instructional Authoring docs (Authorware, ToolBook, etc.), Flash animation, HTML docs, illustrations & graphics, audio clips, video clips, and quiz questions.
An LCMS manages the process of creating, storing and delivering learning content. Typically, the components of an LCMS include: an authoring application (editors), a learning object repository, a dynamic delivery interface (automation that provides content assembly, and administration tools. The following graphic illustrates the role of the LCMS in supporting the workflow of authoring, development and project management.
The benefits of an effective LCMS can be summarized in this way:
-
Rapid Content Development (faster time to market)
- Workflow model
- Reuse model (tools & procedures for automated assembly)
- Tagging, storage & retrieval model
- Template model
-
Integrated E-Learning Platform
- Support of web-standards
- Support of multiple media formats
- Support flexible mixing and matching of authoring / delivery tools & formats
- Ease of administration
-
More Efficient Content Production
- Support of development workflow
- Support of templates & CSS skins
- Support of assessment & data tracking
-
- Ease of content & asset reuse
- Efficient asset management
-
Enterprise Learning Content Management
- Just-in-time access
- Systematic content development for short-term & long-term needs
- Administration of an enterprise content strategy
The following graphic illustrates Cisco Corporation's model of how an LCMS linked to a Dynamic Delivery Engine can automate personalized delivery to individual learners:

Some of the current LCMS products and vendors in 2007 include:
LMS vs LCMS 
The distinction between LMS and LCMS has not always been clear. The first LMS systems to market handled the first order of content management as an integral feature. However, these systems evolved over time through experience in real-world implementation and problem-solving, and as more complex needs of content management emerged.
- The automation for course delivery in LMS has improved as SCORM and AICC standards have been established and widely adopted. These standards dictate how content and learning systems should be designed so that content is sharable among disparate systems.
- The need for a distinct LCMS functionality emerged as the needs of content authors and learning object reuse were defined.
- The concept of Learning Object methodology has evolved and clarified, although it has a long way to go before it achieves its intended goals.
Various vendors claim superiority of their particular LMS or LCMS product. However, the following table provides a comparison of typical functionality in order to understand the broad distinction, and what an integrated system achieves.
|
Key Functionality
|
LMS
|
LCMS
|
Who does it serve?
Primary Targeted Users |
Learners (students & workers), Training Dept Admin, Managers, Instructors, Administrators
|
Content Developers, Instructional Designers, Project Mgrs, Subject Matter Experts (SME)
|
What is the primary goal?
Primary Targeted Services |
Learner Mgt:
Course Publishing & Enrollment
|
Learning Content Mgt:
Author & SME Course Creation
|
| Peformance Reporting of Training Results |
Primary Goal of System
|
------------------------------
|
| User Collaboration |
Learner collaboration
|
Author collaboration
|
| Keeping Learner Profile Data |
Primary Goal of System
|
------------------------------
|
| Sharing Learner Data with an ERP system |
|
------------------------------
|
| Event Scheduling |
|
|
| Competency Mapping — Skill Gap Analysis |
|
|
| Content Creation Capabilities |
Some vendors include this
|
Primary Goal of System
|
| Organizing Reusable Content |
------------------------------
|
Assembly Engine —
Primary Goal of System
|
Creation of Test Questions &
Test Administration |
|
|
| Dynamic Pre-testing and Adaptive Learning |
--------------------------------
|
|
| Workflow Tools to Manage the Content Development Process |
-------------------------------
|
Primary Goal of System
|
Deliver Content by Providing
Navigational Control |
|
|
System Architecture 
The following graphics illustrate the logical framework of a Learning Internet or Intranet portal site that includes both LMS (for content delivery) and LCMS (for content development). Discussion of these specific components has been presented in the section entitled "E-Learning System Architecture."


The following system diagram was suggested by IDC (2001) to illustrate the relationship between LMS and LCMS. Note the user roles: Author, Instructor, Learner and Administrator. Note also that the LMS is designed to support both online and classroom presentation, and can resource CD-ROM and EPSS delivery systems as well. Click on the graphic to see a larger version of the illustration.

Cisco outlines its system distinction between LCMS and LMS in a white paper: E-Learning Content Management vs. Content Delivery.
Automated Course & Lesson Presentation 
The technology infrastructure of E-Learning provides the mechanism for automated course delivery and lesson presentation. Here is a list of the major elements of instruction that are enhanced by this automation.
E-Learning Lesson Presentation
- Self-checks -- questions interspersed within the instruction
- Lesson and module quizzes
- Positive and negative examples
- Mixed media -- text, audio and visual
- Review
- Mnemonic devices
- Content chunking -- breaking up the content into manageable and logical topics and lessons as well as individual nuggets of instruction
- Letting learners practice — with feedback
E-Learning Course Delivery
- Tutorial presentation (receptive & directive learning)
- Guided discovery
- Role-play
- Guided and unguided demonstrations
- Simulations and practice
- Gaming
- Storytelling
- Exploratory learning
- Mentoring

|
|
 |
LMS — LCMS
|
 |
|
|



