|
 Instruction > Instructional Design Instruction > Instructional Design
Instructional Design
|
" The only kind of learning which significantly influences behavior
is self-discovered or self-appropriated learning —
truth that has been assimilated in experience."
Carl Rogers
|
Instructional design is the systematic specification of instruction to include: objectives, presentation, activities, materials, guidance, feedback and evaluation. It applies learning principles to decisions about information content, instructional method, use of media and delivery system. The goal is to ensure instructional quality, effectiveness, efficiency and enjoyment.

The purpose of instructional design is to maximize the value of instruction for the learner — especially the learner's time. Instruction provides a concentration of life-experience into a shortened, optimized time frame and provides feedback to ensure that learning objectives are actually being achieved. Ideally, instruction allows the knowledge, wisdom and skills of an instructor-author to be personally communicated or demonstrated to a learner.
A detailed overview of this process is provided in the section called "The Design Process".
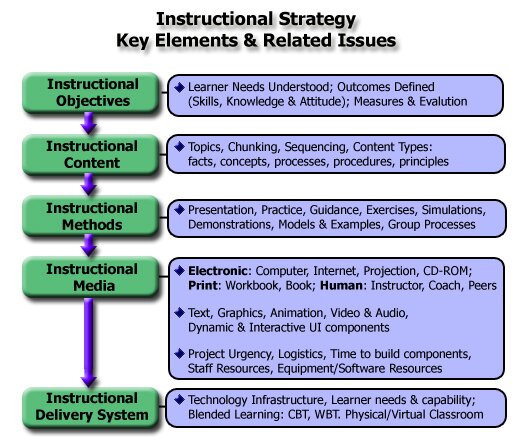
Instructional Strategy: Key Elements & Issues
The Cognitive Design Model provides a systematic approach to developing instructional strategy. Here are the milestones and key elements which must be addressed in order for instruction to be "instructionally sound" — that is appropriate, effective and efficient for the learner :
Cognitive Information Processing
The following Cognitive Information Processing model (CIP) of learning presents a well-established paradigm of cognitive-behavioral psychology. The model articulates the limited capacity of "working memory." Working memory is tasked with the burden of processing incoming information, transferring information to long-term memory and retrieval of information from long-term memory. The concept of "cognitive load" — the amount of work imposed on working memory by a learning task — is based on observations of the functions of working memory.

Cognitive Information Processing (CIP)
The CIP model addresses the following learning issues:
- Cognitive load
- Auditory & visual channels
- Attention
- Rehearsal
- Elaboration
- Mental models
- Schema
- Metacognitive skills
- Motivation

|
|
 |
Instructional
Design |
 |
|
|



